After spending over a decade in the digital display industry, I've seen technologies come and go. But nothing has captured the imagination quite like the transparent LED screen. It's not just a display; it's a window into the future of advertising and architecture. This guide breaks down everything you need to know, from the core technology to practical applications, helping you understand how these amazing screens can transform any glass surface into a dynamic canvas.

Key Insights into Transparent LED Screen Technology
Here's a quick rundown of the most common questions about transparent LED screens for windows.
- What is a transparent LED screen? It's a display that shows video and images while letting you see through it. This is achieved by mounting tiny LEDs on a transparent base, like glass or film, maintaining visibility and allowing natural light to pass through.
- How does it work? The technology places LEDs on transparent conductive material. This allows the pixels to light up and create an image without a solid, opaque background. The space between pixels allows for transparency.
- What's the average cost? It varies. According to 2024 data from LEDinside, the price per square meter for transparent LED screens ranges from $2,500 to $6,000. This depends on factors like pixel pitch (resolution), brightness, and size.
- What is the lifespan? A quality transparent LED screen can last a long time. The typical lifespan is between 50,000 to 100,000 hours, which translates to over a decade of use depending on the operating conditions.
- What's the main difference between screens and film? A transparent LED screen is a rigid, self-contained panel. In contrast, a transparent LED film is a flexible, adhesive layer that can be applied directly onto existing glass surfaces, turning them into a display.
- Are they energy-efficient? Yes, they are. Compared to traditional digital signage, transparent LEDs consume significantly less power because they only use energy for the pixels that are lit, and their high transparency reduces the need for constant, high-power backlighting.
Unpacking the Technology: How Transparent LED Screens for Windows Work
Ever wondered how a window can suddenly spring to life with vibrant video content while you can still see right through it? It's not magic; it's brilliant engineering. The technology behind transparent LED screens for windows is a fascinating blend of materials science and electronics, designed to balance visibility with visual impact. It’s a game-changer for businesses aiming to create unforgettable customer experiences. Let’s dive into the mechanics of how it all comes together.
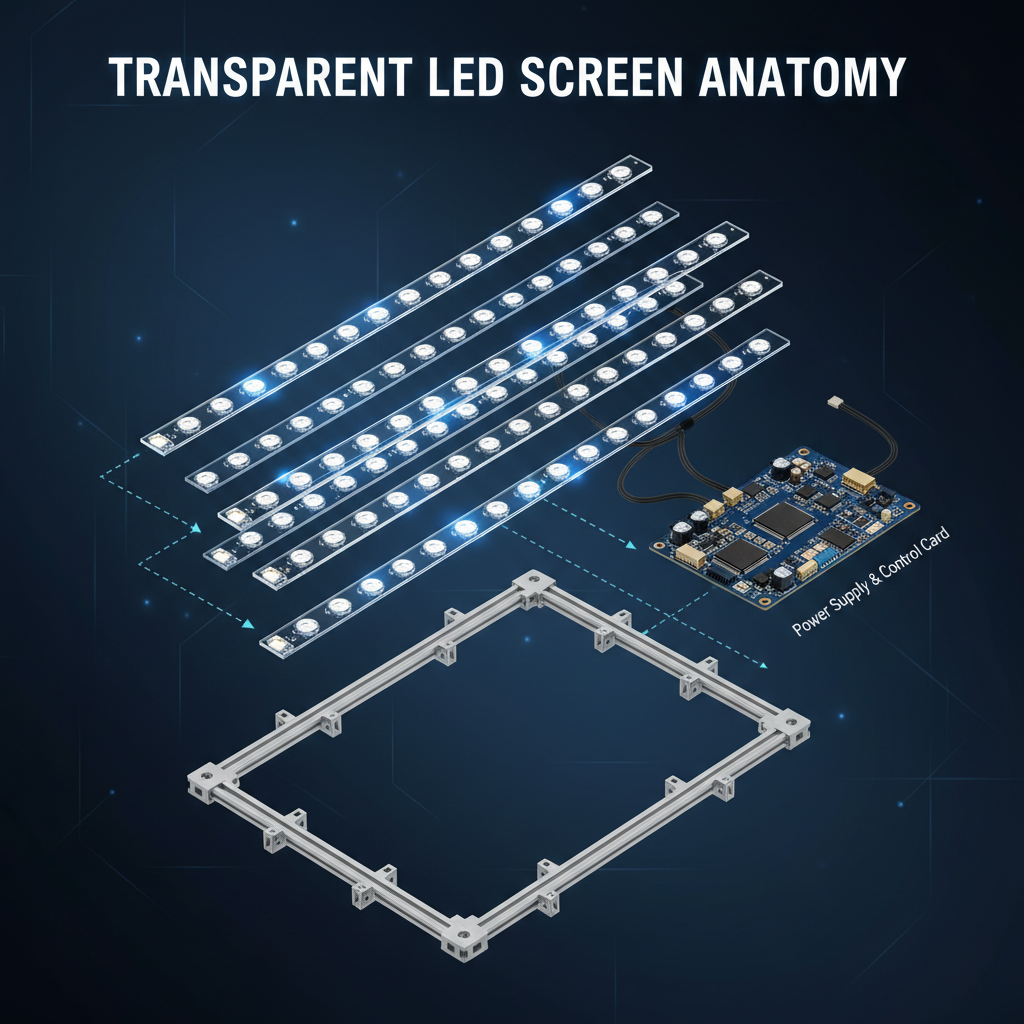
Core Components: The Anatomy of a Transparent LED Display
At its heart, a transparent LED display is simpler than you might think. It’s not one solid piece but an assembly of carefully chosen components.
- LED Lamp Beads: These are the tiny light sources that create the image. They are precisely mounted onto the structural frame.
- PCB Strips: Instead of a solid circuit board, these screens use ultra-thin, almost invisible Printed Circuit Board (PCB) strips to hold the LEDs. This minimalist design is key to maximizing transparency.
- Frame/Cabinet: A lightweight aluminum or steel frame provides structural support for the LED strips and houses the power supplies and control systems.
- Power Supply & Control Card: These are the brains of the operation, receiving data and converting it into the light patterns you see on the screen.
The Science of Transparency: Pixel Design and Light Transmission
The "see-through" effect is the star of the show. It's achieved through a clever design that prioritizes light transmission. Unlike traditional screens that need a backlight and multiple layers that block light, transparent LED displays mount LEDs directly onto a transparent substrate. The empty space between the individual LED pixels is what allows you to see through the screen. The higher the transparency rating (often 60-95%), the more see-through the screen is. This design not only preserves the view but also allows natural daylight to flood the interior space, maintaining the building's original aesthetic.
Understanding Pixel Pitch and Its Impact on High-Resolution Transparent LED Screens
Pixel pitch is a critical specification that defines a screen's resolution and optimal viewing distance. It's the distance (in millimeters) from the center of one pixel to the center of the next.
- Smaller Pixel Pitch (e.g., 2.5mm): This means pixels are closer together, creating a higher-resolution image that looks sharp even from a short distance. It’s ideal for storefront windows where customers are close.
- Larger Pixel Pitch (e.g., 10mm or more): Pixels are farther apart, resulting in lower resolution but higher transparency. This is perfect for large building facades where the audience is viewing from far away.
Choosing the right pixel pitch is a trade-off between image clarity and transparency. A smaller pitch gives you a crisper image but slightly reduces the see-through percentage.
Material Deep Dive: What Are Transparent LED Screens Made Of?
The materials used in a transparent LED screen are just as important as the technology itself. The choice of substrate, LED type, and protective coatings directly influences the screen's performance, durability, and overall quality. At Zhenmei Wisdom, we focus on sourcing and engineering with top-tier materials to ensure our flexible transparent screens deliver exceptional visuals and longevity. Let’s break down the key materials that make these innovative displays possible.
Substrate Materials: PCB, Glass, and Film Options
The substrate is the foundation of the transparent screen, and different materials are used for different applications.
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board): The most common method involves mounting LEDs on narrow, hollowed-out PCB strips. This design offers a great balance of transparency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Glass: Some premium screens embed the LEDs directly within laminated safety glass. This offers maximum durability and a seamless look, making it ideal for high-end architectural installations and railings.
- Film: This is where things get really flexible. A transparent LED film display screen uses a clear, thin polymer film as the substrate. The circuitry is printed onto this film, which can then be applied to any glass surface, curved or flat. It’s a lightweight and versatile alternative.
LED Chip Technology: SMD vs. COB in Transparent Displays
The type of LED technology used also plays a huge role. The two main contenders are SMD and COB.
- SMD (Surface-Mounted Device): This is the most widely used technology in transparent displays. Each "pixel" is a tiny package containing red, green, and blue diodes. SMD technology is mature, reliable, and allows for very small pixel pitches, which is crucial for high-resolution transparent screens.
- COB (Chip-on-Board): A newer technology where multiple bare LED chips are mounted directly onto the substrate. COB offers higher pixel density, better heat dissipation, and a more uniform light output. While still emerging in the transparent display market, it promises even greater durability and image quality.
Protective Layers and Durability Factors for Outdoor Use
For an outdoor transparent LED window display, durability is non-negotiable. These screens need to withstand rain, UV rays, and temperature fluctuations. Manufacturers achieve this by adding protective layers. A conformal coating (often a clear acrylic or silicone resin) is applied over the PCBs to protect the electronics from moisture and dust. Additionally, many screens use UV-resistant materials and robust, corrosion-proof aluminum frames to ensure a long operational life, even in harsh outdoor environments.
Transparent LED Screen vs. Transparent LED Film: A Technical Comparison
When choosing a transparent display solution, one of the first decisions is whether to go with a rigid screen or a flexible film. Both technologies can transform a window into a media display, but they differ significantly in structure, performance, and installation. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right product for your project. A rigid screen might be perfect for a new building facade, while a film could be the ideal retrofit for an existing retail store.
Structural Differences: Standalone Panels vs. Adhesive Film Application
The most obvious difference is in their form factor.
- Transparent LED Screen: This is a modular system built from rigid panels or "cabinets." Each cabinet is a self-contained unit with its own frame, LED strips, and connections. These panels are mounted onto a support structure, often custom-built for the window or wall.
- Transparent LED Film: This is an ultra-thin, flexible display that comes in a roll, much like window tint. It features a self-adhesive backing that allows it to be applied directly onto an existing glass surface. Its lightweight and flexible nature means it can conform to curved glass, opening up creative possibilities.
To retrofit an existing glass facade without altering the building's core structure, a flexible transparent LED film is often the more practical and cost-effective solution.
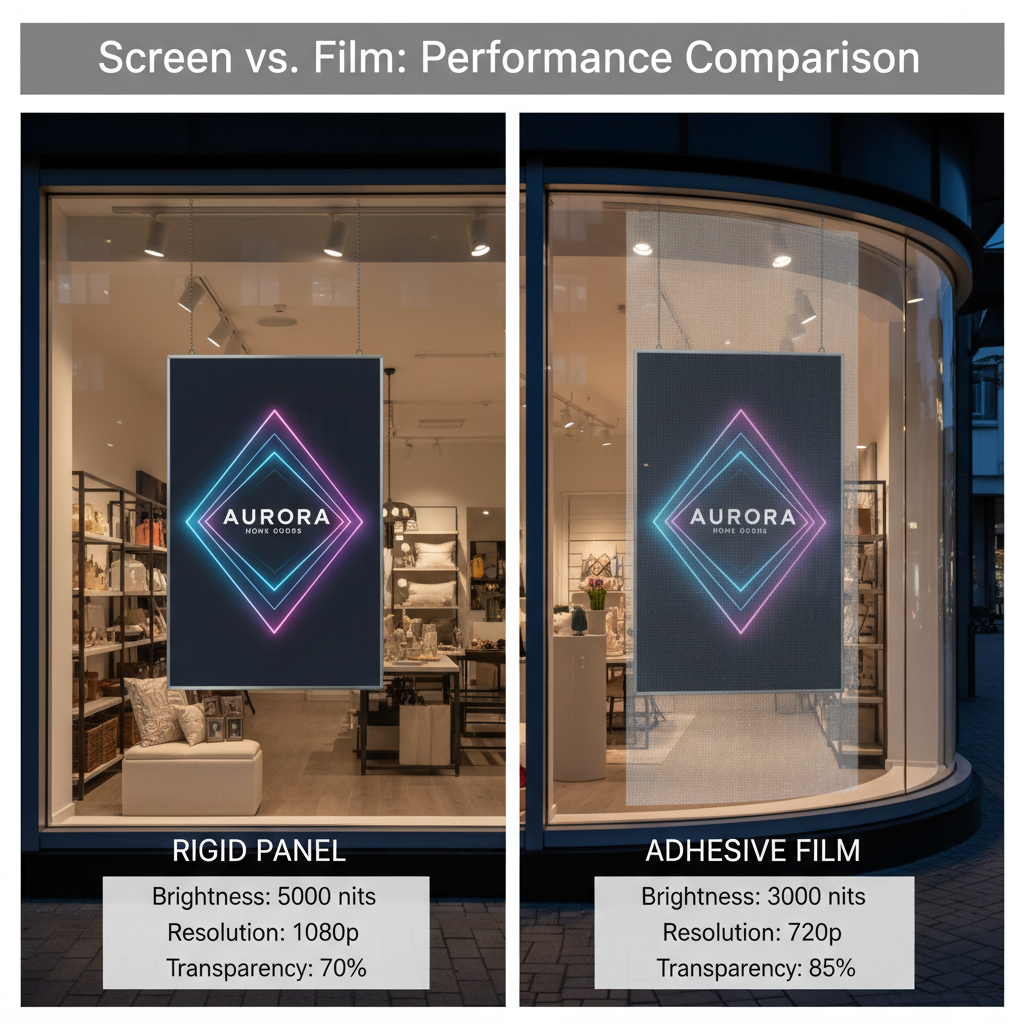
Performance Metrics: Brightness, Resolution, and Transparency Levels
Performance can vary between the two types, and it's important to compare them based on your specific needs.
| Feature | Transparent LED Screen (Rigid Panel) | Transparent LED Film (Adhesive) |
|---|---|---|
| Brightness | Typically higher (up to 7,000 nits), ideal for direct sunlight. | Generally lower (1,000-5,000 nits), best for indoor or semi-outdoor use. |
| Resolution | Can achieve very small pixel pitches (e.g., P2.5) for high-def visuals. | Pixel pitch is often larger, so resolution might be lower. |
| Transparency | Varies from 60% to 95% depending on pixel pitch. | Can achieve very high transparency (up to 95%+) due to its thin profile. |
| Flexibility | Rigid and not suitable for curved surfaces. | Highly flexible and can be applied to curved glass. |
Installation and Maintenance: What's Involved with Transparent LED Film vs Full Screen Display?
Installation and maintenance are major considerations. Rigid screens require a more involved setup, often needing professional installers and a dedicated mounting structure. While very stable once installed, repairing a single panel can sometimes be complex. On the other hand, the installation of a transparent LED film display screen is much faster and simpler—it’s essentially a peel-and-stick process. Maintenance is also straightforward, as individual sections of the film can often be replaced if damaged without taking down the entire display.
Key Applications of Transparent LED Screens in Architecture and Commercial Use
The ability to merge digital content with physical space has made transparent LED screens a powerful tool across various industries. From dazzling storefronts to futuristic building facades, this technology is redefining how brands and architects engage with their audiences. The global market for transparent displays is soaring for a reason—it’s a technology that delivers both aesthetic beauty and commercial value.
The global transparent LED display market was valued at USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18% through 2025, driven by increasing adoption in retail and advertising sectors. (Source: MarketsandMarkets)
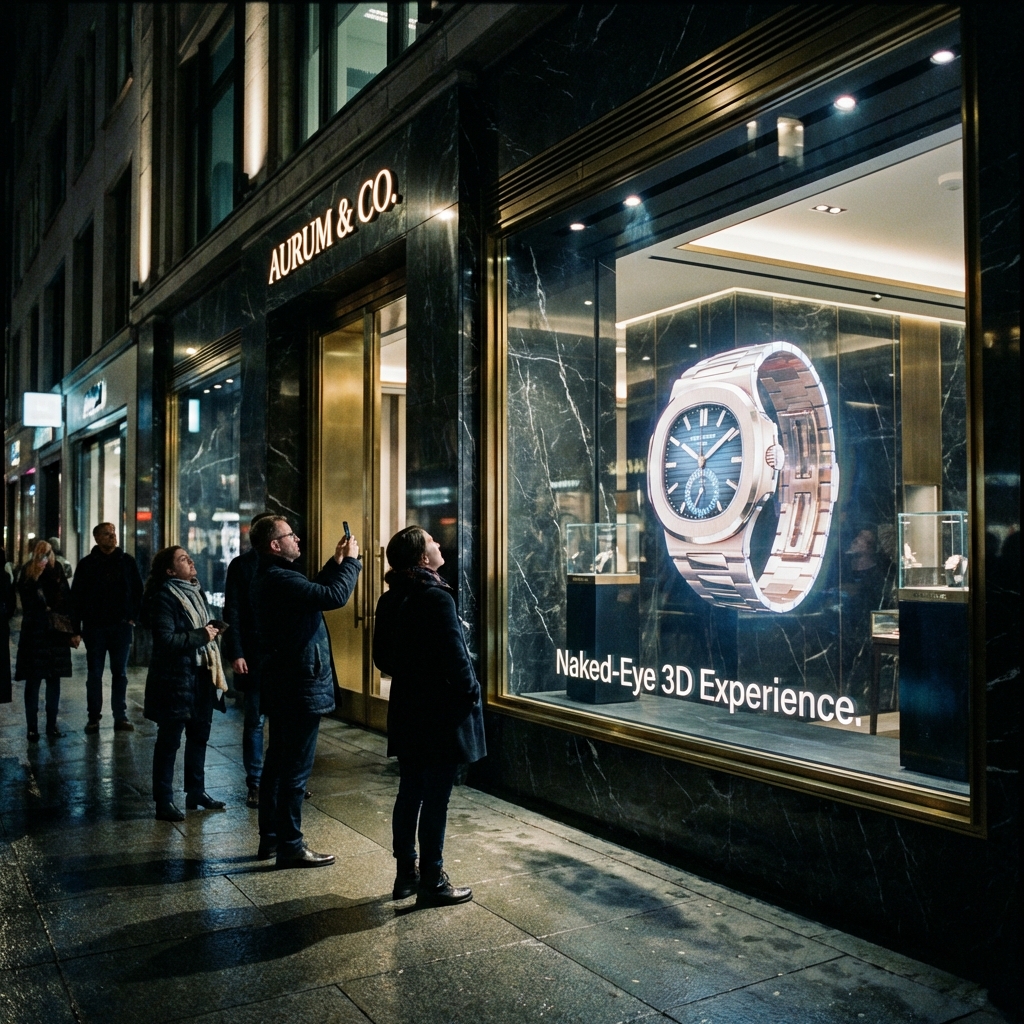
Enhancing Retail Spaces: The Role of Transparent Digital Signage in Storefronts
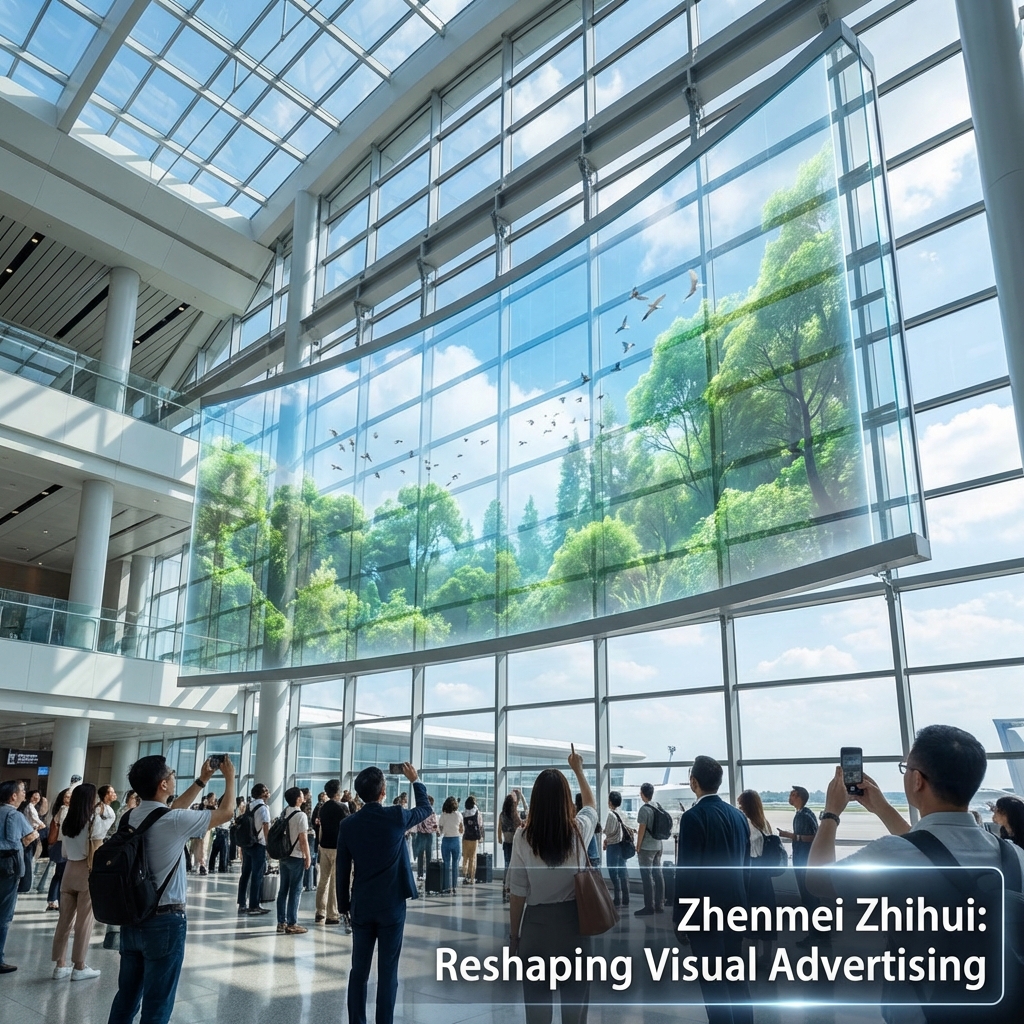
For retailers, the storefront window is prime real estate. Transparent digital signage turns this static space into a dynamic advertising platform without blocking the view into the store. Retailers can run eye-catching promotions, showcase new products with vibrant video, or create immersive seasonal themes. This attracts foot traffic while still allowing potential customers to see the products and atmosphere inside. It maintains an open, inviting feel that solid screens can’t offer, blending the digital and physical shopping experience perfectly.
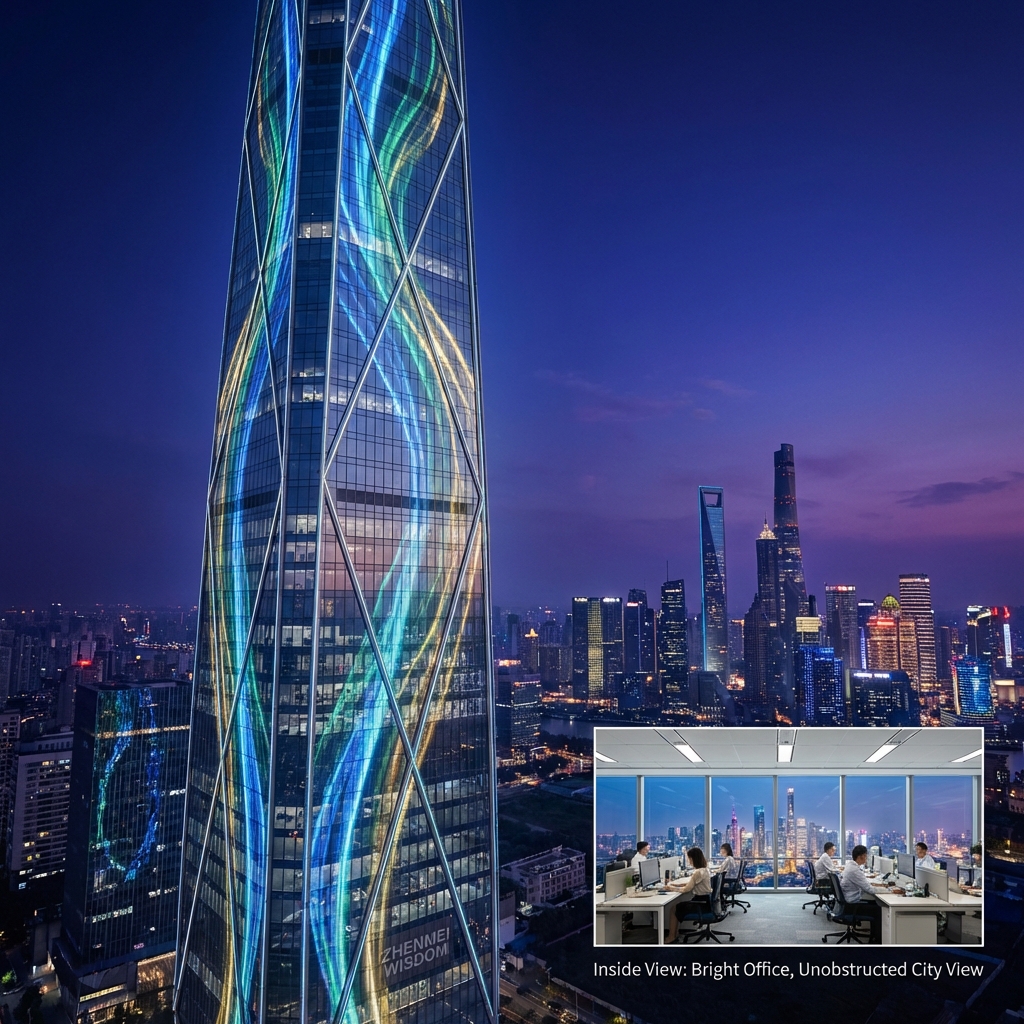
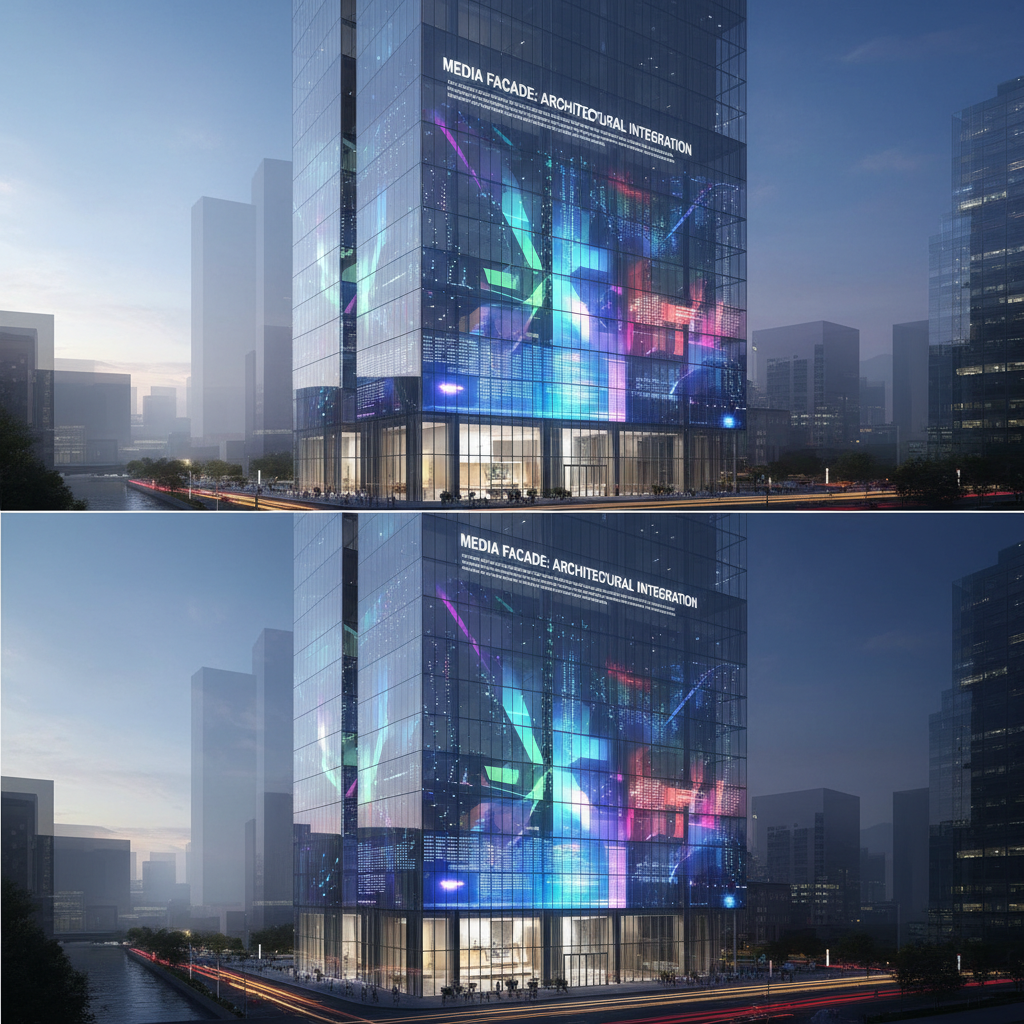
Architectural Integration: Creating Dynamic Glass Facades and Media Walls
Architects are embracing transparent LED display technology to create "media facades." Imagine a skyscraper's entire glass exterior transforming into a colossal screen at night, displaying art or information, yet remaining perfectly transparent during the day. This technology allows buildings to become living, breathing landmarks. It integrates seamlessly into curtain walls, balustrades, and skylights, adding a layer of digital interactivity without compromising the architectural design or blocking natural light for the occupants inside. It’s a powerful way to make a building an icon.

Use Cases in Public Venues: Museums, Airports, and Corporate Lobbies
Public spaces are also benefiting from this technology.
- Museums: Transparent displays can overlay digital information onto physical artifacts. A visitor could look at an ancient vase through a transparent screen that displays its history and origin.
- Airports: They can be used for wayfinding, flight information, and advertising without creating visual clutter or obstructing sightlines in busy terminals.
- Corporate Lobbies: Companies use them to create a stunning first impression, displaying brand stories, welcome messages, or digital art that reinforces a modern, innovative image.
When designing for public spaces, prioritize content that is clear, concise, and enhances the visitor's journey rather than distracting from it.
Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics Explained
Getting the best performance from a transparent LED screen for windows means understanding the key technical specs. Terms like "nits," "contrast ratio," and "refresh rate" might sound complex, but they are crucial indicators of a screen's quality and suitability for your environment. A screen that looks brilliant in a showroom might not perform well in direct sunlight if its brightness isn't high enough. Let's decode these metrics to help you make an informed decision.
Brightness (Nits) and Contrast Ratios for Day and Night Visibility
Brightness is measured in nits (candela per square meter) and is perhaps the most important spec for a window display. For a screen to be visible in direct sunlight, it needs high brightness.
- Indoor Use (e.g., mall interior): 1,000–2,000 nits is usually sufficient.
- Semi-Outdoor (e.g., shaded storefront): 2,000–5,000 nits is recommended.
- Full-Outdoor (direct sunlight): Over 5,000 nits is a must for the content to remain vibrant and visible.
Contrast Ratio is the difference between the brightest white and the darkest black. A high contrast ratio makes images pop and text more readable, especially in bright conditions.
Energy Efficiency: Are Transparent LED Screens an Eco-Friendly Option?
Yes, transparent LED screens are considered an eco-friendly display solution. Their energy efficiency stems from two key factors:
- High Transparency: The screen's see-through nature allows natural light to enter the building, reducing the need for artificial indoor lighting during the day.
- Pixel-Level Power: LEDs only consume power when they are on. Since much of the screen is "off" (transparent), the overall energy consumption is significantly lower than traditional LCD or opaque LED screens that require a constant backlight. This translates to lower electricity bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Integration Capabilities with Smart Window Display Systems and IoT
Modern transparent LED screens are more than just displays; they are smart devices. They can be integrated with smart window display systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). This allows for:
- Remote Content Management: Update promotions, videos, and messages from anywhere in the world via a cloud-based content management system (CMS).
- Interactive Features: Integrate sensors (like touch or motion) to create interactive experiences that engage customers.
- Automated Adjustments: Connect the screen to light sensors that automatically adjust its brightness based on the ambient light, ensuring optimal visibility and energy efficiency at all times.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are transparent LED screens durable enough for outdoor use?
Absolutely. Many transparent LED screens are specifically designed for outdoor use. They are built with IP65-rated (or higher) weatherproof enclosures, UV-resistant materials, and durable components to withstand rain, wind, and extreme temperatures.
What is the typical lifespan of a transparent LED screen?
The lifespan of a high-quality transparent LED screen, such as the innovative LED holographic screen, typically ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 hours. This depends on factors like usage patterns, brightness levels, and how well it is maintained.
How do transparent LED screens compare to traditional LCD displays?
The biggest advantage of transparent LED screens is their transparency. While a traditional LCD screen is a solid black box that blocks the view, a transparent LED display integrates with the environment. It allows for a layered experience, blending digital content with the real world behind it—something an LCD simply cannot do.
References
- MarketsandMarkets, Global Transparent LED Display Market Report, 2023.
- LEDinside, Quarterly LED Display Market Analysis, 2024.
- Display Daily, Technical Whitepaper on LED Lifespan and Reliability, 2023.





